Services
- Fair Value Pricing
- Hedge Effectiveness Test
- Separation of Embedded Derivatives
- Fair Value Hierarchy
- CVA for Derivatives
Overview
- Under the K-IFRS 1039 and 1113, financial instruments without market price has to be valuated with proper valuation technique.
- Establishment of internal valuation procedures as recommended by FSS Accounting Supervision.
- KAP has improved the objectiveness and fairness of the valuation results and has gained market trust by thorough valuation procedure.
Services
- PPA , goodwill, impairment test
- Sensitivity data for Level III footnote disclosure
- Internal and external audit (settlement) support
Overview
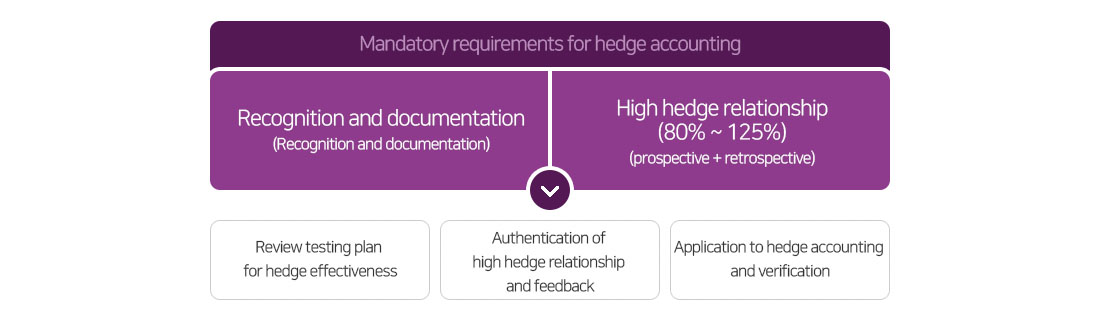
- Hedge Effectiveness Test (HET) verifies whether the hedge is in conformity with IFRS requirement. Shortcut method is no longer acceptable under K-IFRS, prospective and retrospective tests should be conducted
Services
Provision of prompt and reliable HET results for hedge accounting switching from K-GAAP to K-IFRS
Cash Flow Hedge
- Hedge of exposures in cash flow fluctuation accounted for recognized assets and liabilities or highly probable future transaction
Fair Value Hedge
- Hedge of exposure in fair value changes of recognized assets and liabilities or unrecognized commitments
PROCESS / Methodology
Methodology
Dollar Offset Method
| Dollar offset method |
|
|---|---|
| Cumulative dollar offset method |
|
| Measurement of Ineffective Portion |
|
Regression Analysis
- Effectiveness test through regression analysis of changes in fair value of hedged item and hedging instruments with more than 30 hypothetical scenarios
Hypothetical Derivative Method
- Setting identical cash flow condition using same principal, interest rate and currency denomination
- Generating hypothetical derivatives with perfect cash flow hedge at the inception
- Computing the par rate of hypothetical derivative
Additional Service
- Discount rate data: Zero curve data, Swap curve data, Fx rate, Foreign Curve data
- Scenario Test
As the leading derivatives valuation company, KAP conducts the separation of embedded derivatives and compute fair values of CB, BW, EB, CLN, CDO in conformity with K-IFRS requirement.
Overview
- Under K-IFRS 1039 BC37, for consistency purpose, all embedded derivatives not measured in fair value that are recognized in P/L will be accounted separately as derivatives
Service
| Type | Structure |
|---|---|
| CB | Bond (Main Contract) + Conversion Option |
| BW | Bond (Main Contract) + Preemptive Right |
| CLN, S-CDO | Bond (Main Contract) + CDS Embedded Derivatives |
| ELN | Bond (Main Contract) + Option |
PROCESS / Methodology
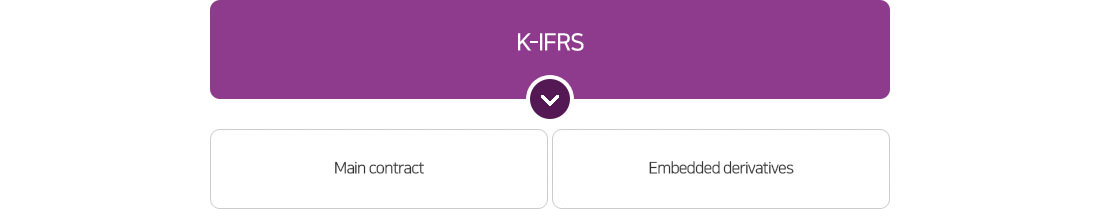
- K-GAAP does not require CB or BW to be separated but under K-IFRS, conversion options and preemptive rights should be separated if they meet the separation requirements
Additional Services
- Separation of fair value and embedded derivatives, sensitivity analysis
- Sensitivity data for Level III footnote disclosure
- Analysis of scenarios to embedded derivatives
KAP offers Product classification codes and pricing manuals for the guideline of hierarchy in financial instruments.
Overview
- K-IFRS 1039 states the quoted price from active market is the best practice of measuring fair value. However, when market price is not available, valuation techniques should be assessed
Hierarchy
- Fair value hierarchy in accordance with the input variables
| Level | Rule |
|---|---|
| Level Ⅰ |
|
| Level Ⅱ |
|
| Level Ⅲ |
|
Service
Determining level and which inputs belong to which level can be very subjective. Therefore, KAP provides product classification of fair value hierarchy, input variables and methods in order to establish clear standard of fair value hierarchy.
Offering Credit Value Adjustment (CVA), reflection of credit risk
Overview
- Under K-GAAP, credit risks are not considered when evaluating OTC derivative valuation.
- K-IFRS 1039 AG82 advises to include credit risks in terms of debt valuation.
- Accordance to K-IFRS, counterparty credit risks should be reflected in terms of fair value of every financial instrument.
Service
For OTC derivatives, CVA is derived from an expected credit loss discounted at risk free rate to reflect counterparty credit risks
CVA(Credit Value Adjustment)
CVA
- Fair value adjustment of derivative contracts to reflect the credit risk of the counterparty
Fait value = Fair value(with no default risk) - CVA)
Method
Reflection on Discount Factor
CVA = ∑CFi(DFrf - DFr)
- DFrf : Discount factor without credit risk reflection
- DFr : Discount factor with credit risk reflection
Reflection of Discount Rate(YTM)
CVA = 100·exp(-rrf) - 100·exp(-rr)
- rrf : Discount rate without credit risk reflection
- rr : Discount rate with credit risk reflection

